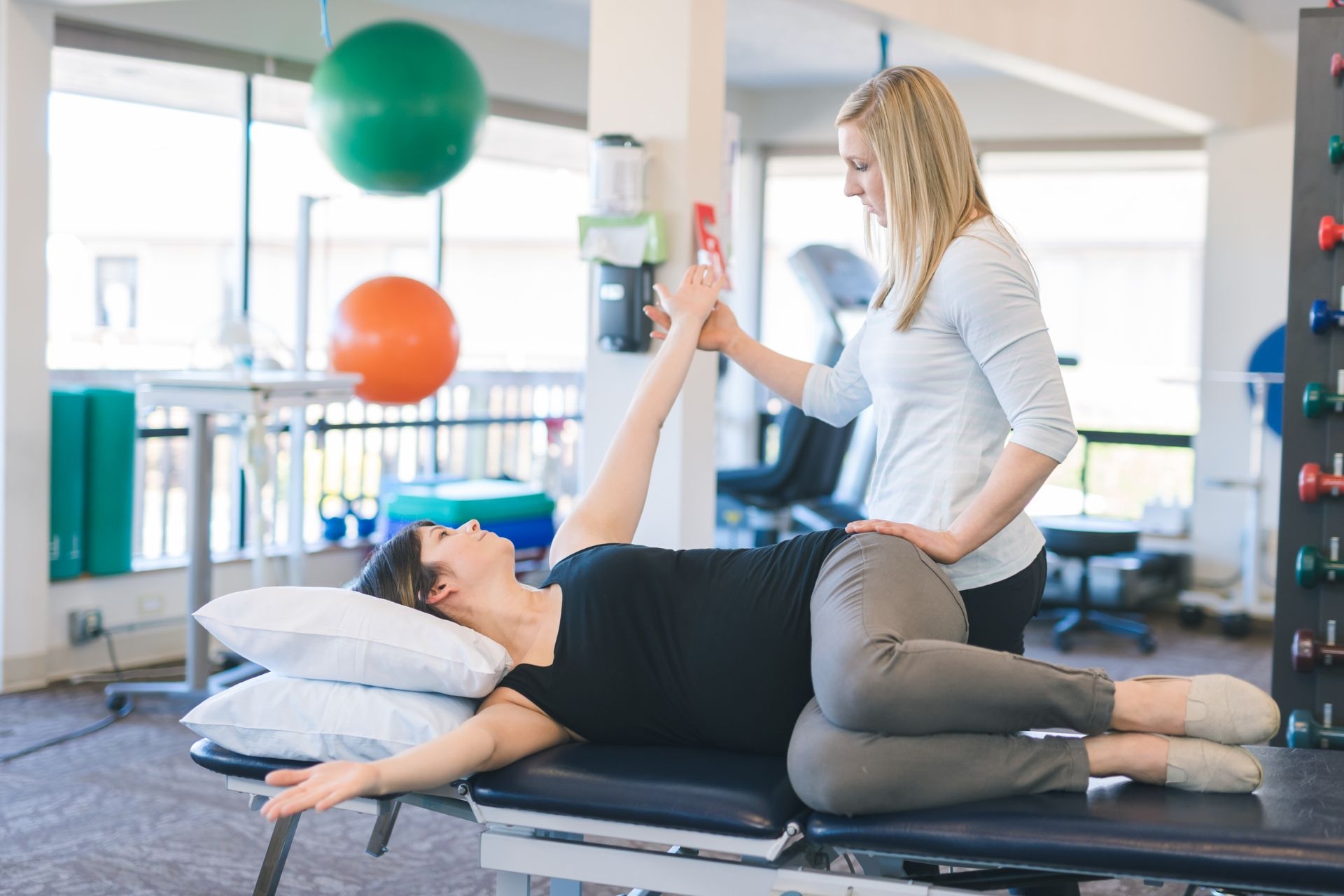


Gait analysis is the process of assessing and evaluating an individual's walking or running pattern. It involves analyzing various aspects of the gait cycle, such as stride length, step width, foot placement, and joint angles. Gait analysis is commonly used in retraining to identify any abnormalities or inefficiencies in a person's gait and develop strategies to correct them. By understanding the biomechanics of an individual's gait, healthcare professionals can design personalized interventions to improve their walking or running technique and address any underlying issues that may be causing pain or discomfort.
Gait analysis can help identify a range of common gait abnormalities. These may include overpronation or underpronation, where the foot rolls excessively inward or outward during the gait cycle, respectively. Other abnormalities that can be identified through gait analysis include leg length discrepancies, asymmetrical arm swing, excessive hip drop, and poor posture. By pinpointing these abnormalities, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to address the specific issues and improve overall gait mechanics.
SF Bay-Area Rehabilitative Healthcare Clinics Lead The Industry In Research and Patient Care
By Professional Physical Therapy Professional Physical Therapy is proud to announce the celebration of its 25th anniversary, January 2024, marking a quarter-century of providing exceptional care and rehabilitation services to their communities throughout New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire. Since the opening of their first clinic in 1999, Professional has been dedicated … Continued The post Professional Physical Therapy Celebrates 25 Years of Excellence in Patient Care appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-12-26
By Professional Physical Therapy In today’s fast-paced world, finding a balance between staying active and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be challenging. Yet, within these challenges lie numerous opportunities to transform our routines and bolster our well-being. We unveil 25 essential tips that serve as steppingstones toward a more active and healthier lifestyle. Each tip … Continued The post 25 Essential Tips to Live a More Active & Healthy Life appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-12-26
Gait retraining plays a crucial role in improving athletic performance. By analyzing an athlete's gait, healthcare professionals can identify any inefficiencies or abnormalities that may be limiting their performance. Through targeted interventions and exercises, athletes can work on correcting these issues and optimizing their gait mechanics. This can lead to improved efficiency, reduced risk of injury, and enhanced overall performance. Gait retraining can also help athletes develop better running or walking techniques, such as increasing stride length, improving foot strike patterns, and optimizing joint angles, all of which can contribute to better athletic performance.
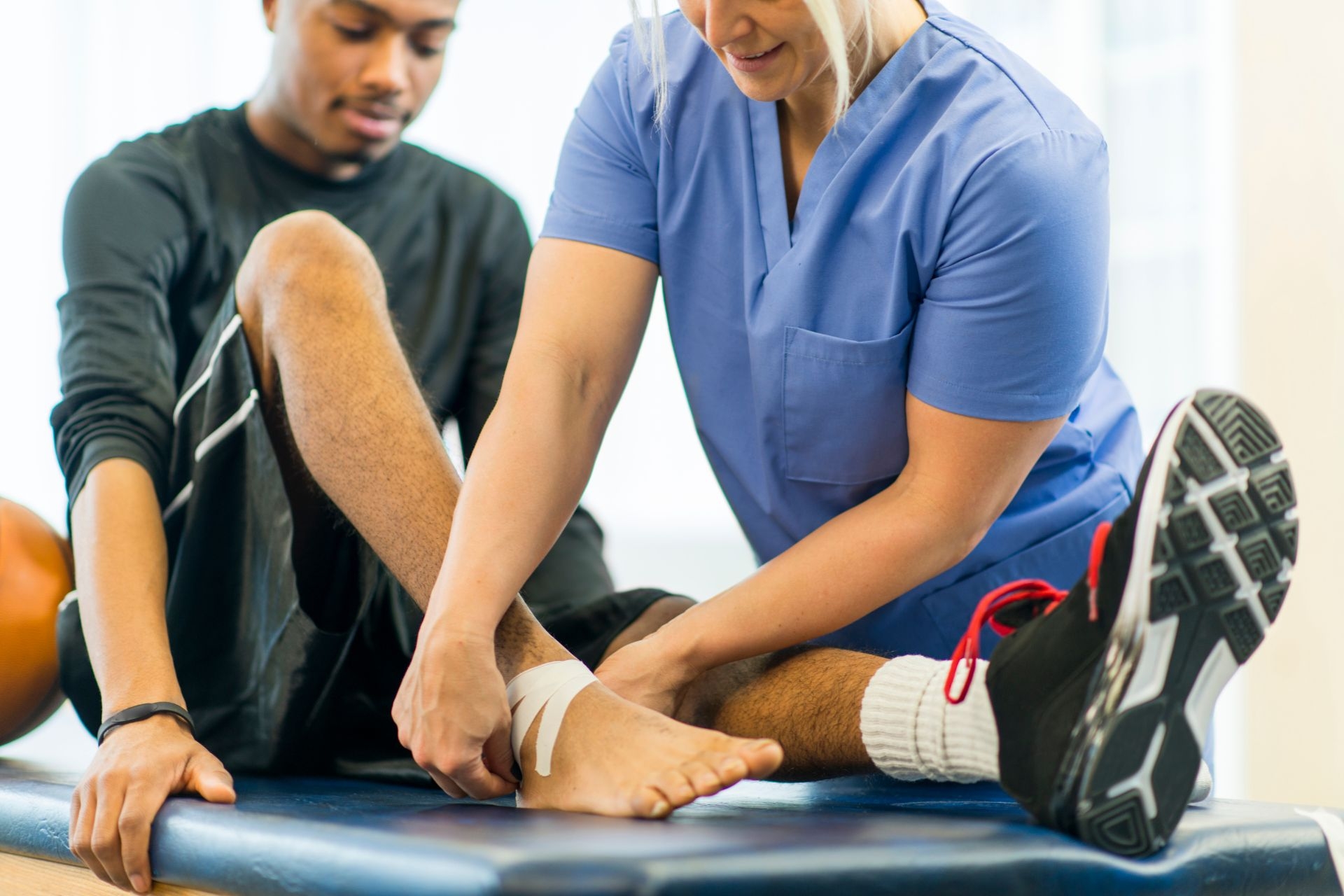
There are various techniques used in gait retraining, depending on the specific needs and goals of the individual. These techniques may include strengthening exercises to address muscle imbalances, stretching exercises to improve flexibility, balance training to enhance stability, and proprioceptive training to improve body awareness and control. Additionally, gait retraining may involve the use of orthotics or footwear modifications to correct foot alignment and provide support. Video analysis and biofeedback techniques can also be used to provide real-time feedback and help individuals make adjustments to their gait mechanics.
Yes, gait analysis and retraining can be highly beneficial for individuals with neurological conditions. Neurological conditions such as stroke, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and cerebral palsy can often affect an individual's gait and mobility. Gait analysis can help identify specific abnormalities or compensatory movements that may be present in these individuals. By designing targeted interventions and exercises, healthcare professionals can help improve gait mechanics, enhance balance and coordination, and promote overall functional mobility in individuals with neurological conditions.
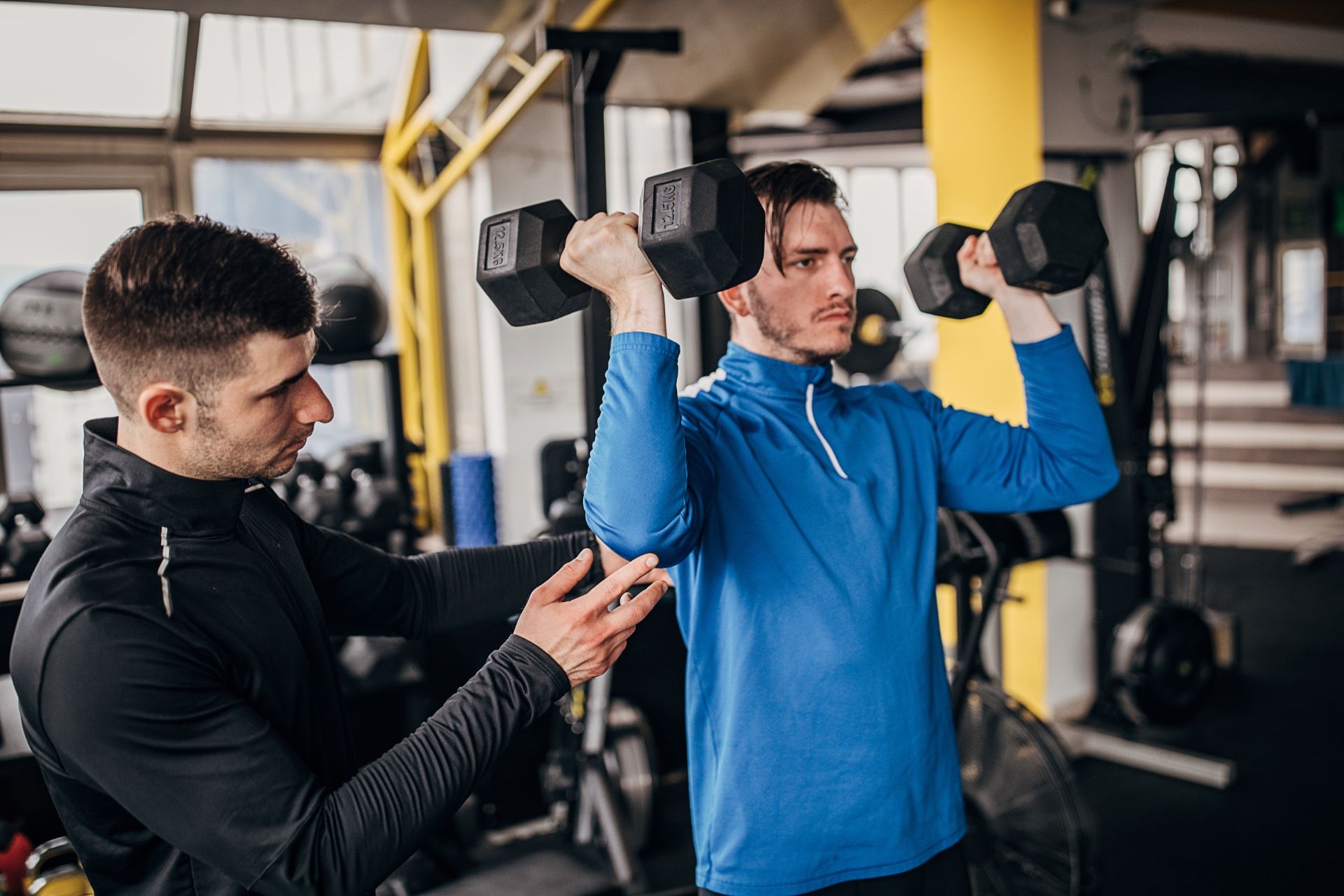

Like any form of physical intervention, gait retraining does come with potential risks and side effects. These may include muscle soreness or fatigue as the body adjusts to new movement patterns, temporary changes in gait mechanics as individuals adapt to the retraining process, and the possibility of exacerbating existing injuries if not properly managed. It is important for healthcare professionals to carefully monitor and assess individuals undergoing gait retraining to minimize these risks and ensure a safe and effective rehabilitation process.
The time it takes to see improvements in gait after undergoing retraining can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the gait abnormality, the individual's commitment to the retraining program, and their overall physical condition. In some cases, individuals may start to notice improvements in their gait within a few weeks of starting retraining, while others may require several months of consistent practice and intervention. It is important to remember that gait retraining is a gradual process that requires patience and persistence. Regular reassessment and adjustments to the retraining program may be necessary to achieve optimal results.
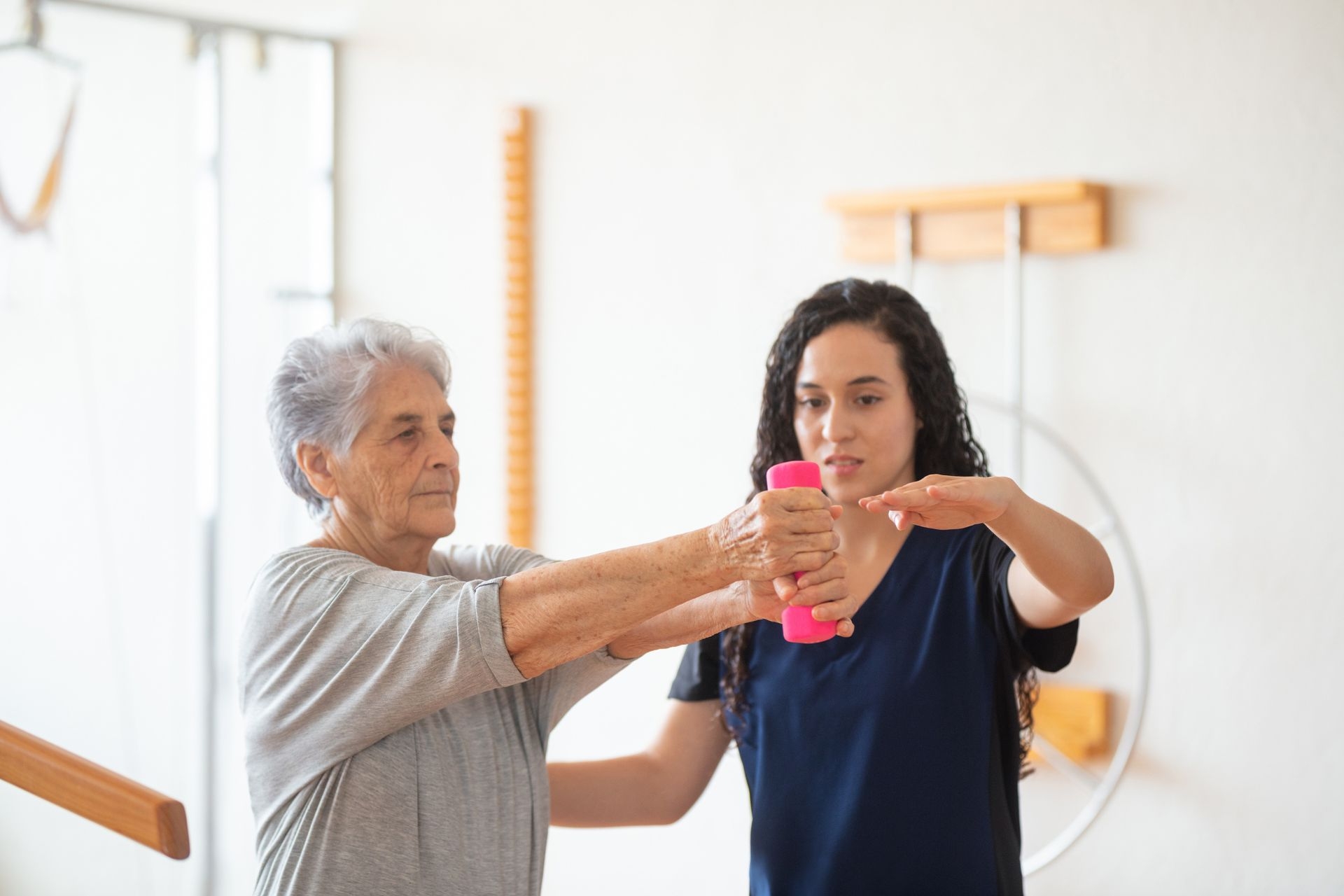

Yes, there are specialized techniques for improving hand function in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in this regard, as it focuses on enhancing the ability to perform daily activities and tasks. Therapists may employ various techniques such as joint protection strategies, which involve teaching individuals how to minimize stress on their joints during activities. They may also use splinting to support and stabilize the affected joints, allowing for improved hand function. Additionally, therapists may recommend exercises and stretches specifically designed to increase strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the hands and fingers. These techniques, combined with medication management and other treatments, can significantly improve hand function and overall quality of life for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
The most common exercises prescribed in physical therapy for rotator cuff injuries include a range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and stretching exercises. Range of motion exercises aim to improve the flexibility and mobility of the shoulder joint, such as pendulum exercises, shoulder circles, and wall climbs. Strengthening exercises focus on building the strength of the rotator cuff muscles, such as external and internal rotation exercises with resistance bands, scapular squeezes, and shoulder presses. Stretching exercises help to improve the flexibility of the muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint, such as cross-body stretches, sleeper stretches, and doorway stretches. These exercises are often tailored to the specific needs and limitations of the individual patient, taking into account factors such as the severity of the injury, the patient's age and overall health, and any other existing conditions or injuries.
Foam rollers offer a multitude of potential benefits in the realm of physical therapy. These cylindrical tools, made of foam, can be used to apply pressure and massage various areas of the body, aiding in the release of muscle tension and promoting relaxation. By targeting specific muscle groups, foam rollers can help improve flexibility, increase range of motion, and enhance overall mobility. Additionally, foam rolling can stimulate blood flow and circulation, which can facilitate the healing process and reduce inflammation. This self-myofascial release technique can also help alleviate muscle soreness and prevent injury by breaking up adhesions and scar tissue. Moreover, foam rollers can be utilized for balance and stability exercises, enhancing proprioception and core strength. Overall, incorporating foam rollers into physical therapy sessions can provide patients with a versatile and effective tool for improving their physical well-being.
Yes, there are specialized exercises that can help improve core stability in individuals with lumbar disc herniation. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles surrounding the lumbar spine, including the transversus abdominis, multifidus, and pelvic floor muscles. Examples of such exercises include pelvic tilts, bird dogs, dead bugs, and planks. These exercises help to improve core stability by increasing the activation and strength of the deep stabilizing muscles, which in turn helps to support the lumbar spine and reduce the risk of further injury or pain. It is important for individuals with lumbar disc herniation to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified exercise specialist before starting any exercise program to ensure that they are performing the exercises correctly and safely.
Yes, there are specialized interventions for managing lymphedema in physical therapy. Physical therapists who specialize in lymphedema management use a variety of techniques and modalities to help reduce swelling and improve lymphatic flow. These interventions may include manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, exercise programs, skin care, and patient education. Manual lymphatic drainage involves gentle, rhythmic massage techniques that stimulate the lymphatic system and promote the movement of lymph fluid. Compression therapy involves the use of compression garments or bandages to apply pressure to the affected area, helping to reduce swelling and improve circulation. Exercise programs are tailored to the individual's needs and may include aerobic exercise, resistance training, and stretching to improve muscle strength and flexibility. Skin care is an important aspect of lymphedema management, as it helps prevent infections and skin breakdown. Patient education is also a key component, as individuals with lymphedema need to learn how to manage their condition on a daily basis, including self-care techniques and strategies for preventing exacerbations. Overall, these specialized interventions aim to reduce swelling, improve function, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with lymphedema.